DES Microlearning Videos
This is a comprehensive introduction to the world of digital transformation. This course in Microlearning format covers topics from the enabling technologies, to the transformation roadmap for strategy, to examples of useful management tools and techniques to help you.
You may prefer the Microlearning format, which is easy to consume on the go in smaller bites, on any device. These 126 pieces of Microlearning are useful for independent study, or as a revision aid to complement the 36 corresponding eLearning modules for The Digital Enablement Suite.
Contents Table

How Will AI Affect Employment
As Artificial Intelligence continues to enter every aspect of our lives, what is AI’s effect on employment? This module summarizes a variety of perspectives from global surveys and thought leaders. (Duration 5:10)
What Are The Barriers to Using AI
While AI is growing in its adoption and popularity, it is not a fast and easy journey. Some barriers to using AI remain. We explore and explain the key factors preventing the widespread use of AI. (Duration 1:33)

The Impact of AI on Society
Does AI benefit society, or does it pose a threat to such things as privacy and self-determination? How can these be assessed and what checks and balances are needed. (Duration 7:37)

Superintelligence
An ever-present hope and fear about AI is that its combined processing power could become super intelligent. This intelligence could outpace human capacity for thought. Would this be good or bad? We investigate some current thinking on this. (Duration 8:43)

The Four Types of AI
There are four types of AI, each increasingly sophisticated. We explain these and summarize where we are now, and where we may be headed. Full of opportunity, but possibly also scary. (Duration 5:17)

Introduction to AR, MR, and VR
Most people are aware of Augmented, Mixed and Virtual Reality. In all evolving technologies, terms and their definitions become blurred. We provide clear definitions of how these technologies relate to each other. And introduce some of their current and future applications. (Duration 10:07)

AR, MR, and VR Elaborated
So how will Augmented, Mixed and Virtual Reality come together in the future? Using Milgram’s virtual reality continuum as a framework, we detail the current states between the real and virtual worlds and explore the challenges. (Duration 10:02)

Introduction to Automation
Automation is often perceived as the platform where the key enabling technologies of digital transformation come together. We introduce the two types of automation. Most of us know generally about Industrial Automation, but not all of its variants. Fewer of us know about Software Automation, which is growing in adoption and sophistication. (Duration 9:04)

Industrial Automation
Industrial Automation has been around since the 1970’s, when robotic automation was introduced. Advances in technology have helped evolve this Fixed Automation into Programmable Automation and now Flexible Automation. We explore these types of Industrial Automation and their typical uses. (Duration 6:41)

Software Automation
Software Automation replaces the repetitive tasks of human operators, releasing them to do higher value work. Using “bots” to replace human operators, automation occurs at the software level. This results in increased efficiency and creates a bridge between legacy and modern digital systems. (Duration 7:22)

Introduction to Big Data
The digital age brings with it a data explosion. Much if it is either unstructured, or just too large for traditional database technologies to make sense of. Big data is the technologies and approach to coping with this data explosion. We provide an overview of how we got here, and how Big Data helps us cope with this data explosion. (Duration 4:07)

Big Data Elaborated
A deeper dive into the attributes of Big Data. We explore the 4 V’s of Big Data and describe the convergence of technologies and business imperatives which make Big Data timely and necessary. (Duration 6:52)

Introduction to Blockchain
We are evolving from bits and bytes into a network of value and trust. With blockchain, we can establish and transfer ownership, keep records permanently, and validate transactions. All of this can be accomplished without the traditional and historical intermediaries, such as governments, financial institutions, escrow companies, and notaries. (Duration 6:12)

Blockchain Elaborated
We explore the 4 key functions of a blockchain: digital currencies; record-keeping; securities and smart contracts. Here, we highlight the use cases, in several key industries or domains. Though most experts agree that the greatest immediate impact is on the Banking and Insurance industries. (Duration 9:25)

Introduction to Cloud Computing
For developers, cloud computing provides increased amounts of storage and processing power to run the applications they develop. But Cloud Computing is more than just a technology. We explain why. (Duration 13:09)

Introduction to Cold Calling
Let us introduce you to Cold Calling Essentials. As a consultant or as a salesperson, without the first conversation with a new customer, you cannot instigate change, you cannot create a new relationship, and you cannot grow a business. (Duration 5:24)

Cold Calling Guidelines
Cold Calling essentials are the same as those required to be an entrepreneur. It can be liberating, empowering, and fulfilling. And it is a technique that can be easily taught, personalized, and transferred. It is more about Attitude than Aptitude. Let us set some essential guidelines to help you do your first cold call. (Duration 4:32)

Dealing With Cold Call Objections
There are several possible objections you will have to deal with while cold calling. In general, they can be classified in five categories. We provide you with practical approaches and sample scripts to deal with each. (Duration 3:22)

Overcoming Fear of Rejection in Cold Calling
Most of us are held back in our sales efforts by the fear and rejection associated with cold calling. Yet there is a handful of simple rules you can follow to overcome this. This module breaks down and explains the Do’s and Don’ts in Cold Calling. (Duration 5:44)

Why is Communicating Important in Consulting
Most of our working time is spent in some form of communication, some studies suggest upwards of 65 percent. We constantly read and write memos and send and respond to emails, on internal and external chat and sharing systems. Business cannot operate without effective communication. (Duration 8:54)

What Is Effective Listening
As much as effective writing and speaking are important in communication, the most important skill is effective listening. Sadly, we only listen with 25 percent efficiency. To help us do better, we provide five simple and effective rules to follow when listening to others. (Duration 2:41)

What Is Non-verbal Communication
As much importance as we place on effective verbal communication, it is crucial to understand that the non-verbal clues we provide speak the loudest and last the longest. We explain what these are, and how to use them to make your communication more effective. (Duration 5:37)

Writing Effectively
In the workplace, we have information overload. Information seems to come from everywhere. With so much information coming our way, we do not have the time to read all of it, unless it grabs our interest. To do this, there are 10 simple guidelines we must keep in mind. (Duration 7:43)

Tips for Public Speaking
If there is one area where most individuals have a natural and almost inborn fear, it is public speaking. Statistics indicate that more than 75 percent of people have stage fright when going in front of the public. We offer some practical tips to overcome this. (Duration 4:04)

What Is A Business Case
A Business Case is a comprehensive effort to obtain approval or financial commitment to a project of any type. We explain some of the different forms a business case can take, and who is responsible for preparing it. (Duration 11:56)

Developing A Business Case
There are many ways to structure your thoughts and assemble the facts and information required to help you write the business case. However, let us introduce you to the eight steps you need to go through before you start writing it. (Duration 13:06)

Essential Sections of a Business Case
Business cases vary widely in size, form, and level of detail. Regardless, there are eight essential sections every business case must contain. Here, we introduce and explain each of these sections. (Duration 9:44)

Digital Transformation Challenges and Opportunities
Data, digital customer engagement, integrated DX strategy, and people are among the key challenges we face in digital transformation. Yet these challenges also offer up opportunities. We explain what they are and how you can start to embrace them. (Duration 7:30)

The Four Drivers of Digital Transformation
Any form of business transformation that a company embarks on should be guided by clear managerial goals and direction, targeting business benefits, on a clear roadmap and timeline. There are four major drivers behind digital transformation. (Duration 5:13)

The Key Enablers of Digital Transformation
There are eight key enablers of digital transformation. These enablers include Cloud Computing and the Internet of Things. But do you know what the others are? Find out here. (Duration 4:05)

What is an Effective Presentation
Presenting is a skill, developed through experience and training. 90 percent of what we learn is through what we see, or watch, or read, and what we hear. So, what makes a presentation effective? Watch here and learn. (Duration 9:55)

How To Overcome Your Fear of Presenting
Most people have a natural fear of presentations and public speaking. Funny as it may seem, statistics indicate that people fear presentations more than death. Good speakers are not born, they practice and rehearse, and their skills come from experience. Learn more about how. (Duration 3:02)

Conducting an Effective Presentation
How do you prepare for and conduct an effective presentation? We offer simple and practical guidelines that will help you make sure your message gets across. (Duration 12:35)

Identifying Business Issues and Opportunities
In a target-rich environment, there are more opportunities than you could ever handle. Generally, though, not all opportunities are right for you or your company. So the critical part is identifying opportunities that are right for you. Find out how you do that. (Duration 5:18)

Porter's Five Forces
Porter’s Five Forces Framework is a tool for analyzing the competition of a business. It draws from industrial organization economics to derive five forces that determine the competitive intensity and, therefore, the attractiveness of an industry in terms of its profitability. Use it as a tool to help you assess your opportunities. (Duration 15:53)

The BCG Matrix
The BCG Matrix is a portfolio planning tool to assess a company’s market position by assessing its product range and potential. Businesses, products, or services classified as low or high performers depending on their market share and market growth rate. Another tool to use in identifying and qualifying opportunities. (Duration 8:33)

The 5 C's of Marketing
To satisfy customer needs in a profitable way, a company should first understand the external and internal situation it faces, its customers, the market it operates in, and its own capabilities as well as its limitations. Most often, situation analysis, known as the 5C’s of Marketing, is used to gain this insight. (Duration 4:16)

SWOT Analysis
Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities and Threats give us an internal and external perspective on a company. We can adopt the point of view of potential customers to use this new perspective to spot issues and opportunities. (Duration 5:06)

Introduction to Digital Project Management Methodologies
In this module, we will introduce you to some of the most current and common digital project management methodologies, and how to choose the right one. (Duration 17:06)

What Is Digital Project Management
Simply said, it is making things happen in the digital world we live in today. The target of every project is different, but the overall goals and objectives are to use digital tools and concepts, to grow business and the bottom line, and to achieve a satisfactory return on investment from the project. (Duration 7:49)

What Is A Digital Project
Most people immediately think of websites, content, online advertising and marketing campaigns, social media, events, and videos. While this is of course true, a digital project is much more than that. In today’s world, any business transformation in a company touches the digital world. (Duration 1:36)

DPM Requirements and Responsibilities
The responsibilities typically assigned to a digital project manager include the following:
- Client and stakeholder management
- Responsibility for the quality of user and customer experiences
- Design, development, and oversight of the project strategy
(Duration 5:19)

Overview of DPM Methodologies
For many digital projects, a rigid standardized methodology, like PM BOK is overkill. Often, a mix of principles, themes, and processes is a better way to go. This module will give you an overview of the different digital project management methodologies. (Duration 10:57)

DPM Tools
Cloud-based project management and collaboration tools allow project managers to harness the full power of digital project management. Serving as a single source of truth, they show you exactly where the project status stands in real time. Learn more here. (Duration 2:15)

Project Scope
Project scope describes the product, processes, or services to be delivered. Completion or success of the project is measured against the stated project requirements. These define the features or functions of the process or product. (Duration 3:15)

Managing Project Scope
If we do not manage project scope properly, we will have scope expansion. This is also referred to as scope creep and has been long identified as one of the major contributing factors to failed projects. (Duration 13:45)

Collecting Project Requirements
This module describes the inputs to the project requirements. We describe the key information sources and plans which need to form integral parts of the project scope. This is fundamental to managing project scope and managing stakeholder expectations. (Duration 9:36)

Managing Stakeholder Expectations
A stakeholder is a person or part of a group who has a vested interest or “stake” in a project or initiative. They have expectations. This is a strong belief that somethings will happen in the future. Or that someone or something will help them achieve the things they expect to happen. Learn how to manage these expectations. (Duration 11:46)

Aligning Stakeholder Expectations
Stakeholder expectation management is the process and all related activities of communicating with stakeholders and managing their expectations and concerns. This meets the stakeholder needs, addressing issues, resolving conflict situations, and achieving the project goals and objectives. This is how you stay aligned. (Duration 11:45)

Keys to Leadership Success in Virtual Teams
Leading digital projects today usually requires managing a virtual team. Our success in being able to overcome the tyranny of distance can be determined by how well we understand and use the key factors in managing virtual teams. Learn more here. (Duration 8:40)

Required Skills in Virtual Teams
Many skills are required for virtual teams to be effective and successful. Here we present what we believe to be the four most important skills to look for in your virtual teams. (Duration 5:19)

Success Factors in Virtual Teams
There can be many success factors for virtual teams. Obviously, distance, time zones, cultures, and language all must be carefully managed. Here we explain what we believe to be the top six success factors for effective virtual teams. (Duration 3:56)

Virtual Team Types
Not surprisingly, there is not just one type of virtual team. There are as many types of teams as there are types of work they must perform. But they can be broadly grouped, and each type will require a slightly different approach and emphasis. (Duration 6:21)

Managing Your Time Effectively
Time Management is the process of allocating time effectively, so that the right amount of time is associated with the most appropriate, and relevant, activities. For instance, to save time in what we do, and how we perform tasks. Or to reduce the stress in our daily life. Or to function more effectively in our job. (Duration 4:26)

Organizing Your Time
Some people’s lives seem smooth, well oiled, and extremely organized. Other people are so disorganized that they are never able to bring order into the chaos of their life, and as a result they appear totally ineffective. The difference is how well they organize and use their time. Learn more about how. (Duration 12:48)

Managing Goals
Managing your time is highly dependent on a process, to help you set and accomplish your goals. Setting goals can be considered somewhat of an art. For a goal to be effective, it needs to be specific and measurable, and should be motivating. Learn more about managing your goals. (Duration 5:48)

Creating A Task List
To manage your time better, write down every outstanding and open item on a task list. Sometimes, this can be daunting and overwhelming, and you will need to accept that some of the tasks cannot be completed without help. (Duration 4:46)

Differences Between DX Project Sponsorship and DX Project Management
In this module, we address what it means to own or be responsible for a digital project or initiative, and how to be successful in its execution. There are many ways where a digital project is different from any other type of project that an organization has already undertaken. (Duration 8:13)

Roles and Responsibilities of a Digital Project Sponsor
The best definition of a project sponsor is a person who is assigned (or assumes) the overall accountability for the project. The project sponsor needs to ensure the delivery of expected business benefits and ROI. Find out more about what distinguishes PMs and sponsors, and why it is important. (Duration 6:22)

The Relationship Between The DPM and The Digital Project Sponsor
The project sponsor and the project manager are inextricably linked to deliver the project successfully and to derive the intended benefits and value. It is an absolute MUST to trust in each other. They should agree on rules of engagement, mutual expectations, roles, and responsibilities. (Duration 18:14)
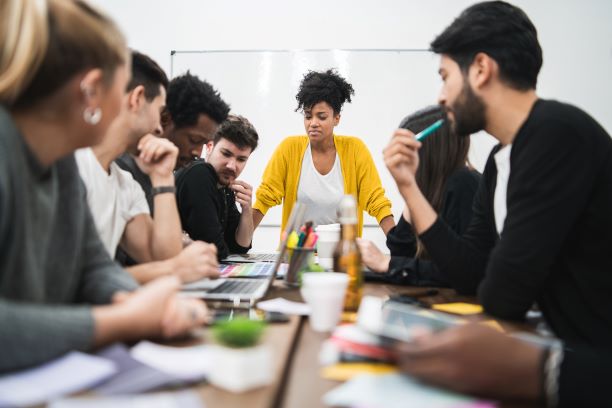

The Five Types of Business Meetings
There are many different types of meetings. However, we can generally categorize business meetings in 5 types. Each of them has a different purpose, process, and outcomes. As a result, each of these requires different preparation and communication. (Duration 2:33)
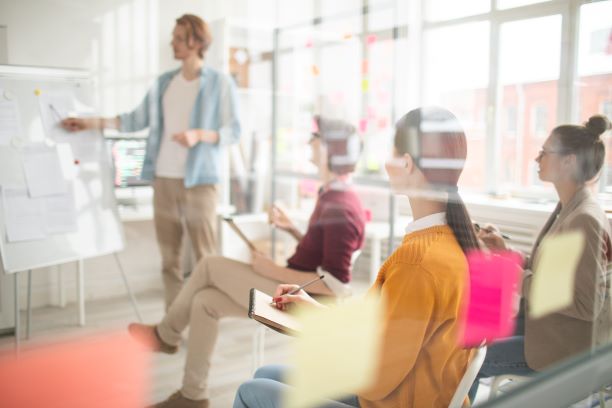

Preparing for a Meeting
Leader, facilitator, recorder, and participant are the four roles in any meeting. Proper preparation for any meeting is essential. Learn about the specific responsibilities of the four roles, in preparation for a meeting. (Duration 5:24)
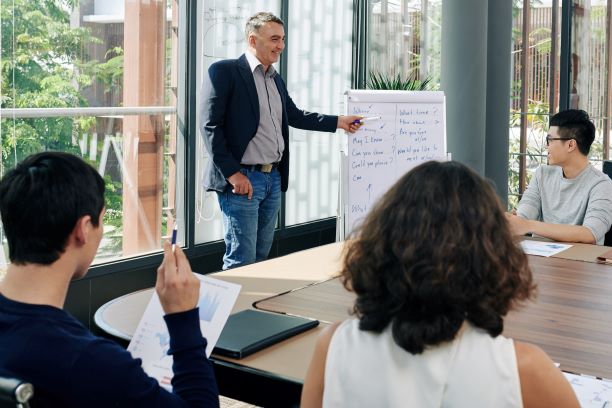

Conducting a Meeting
Leader, facilitator, recorder, and participant are the four roles in any meeting. When they play their parts well, our meetings are productive and effective. Conducting effective meetings requires some simple preparation and role clarity. (Duration 7:34)
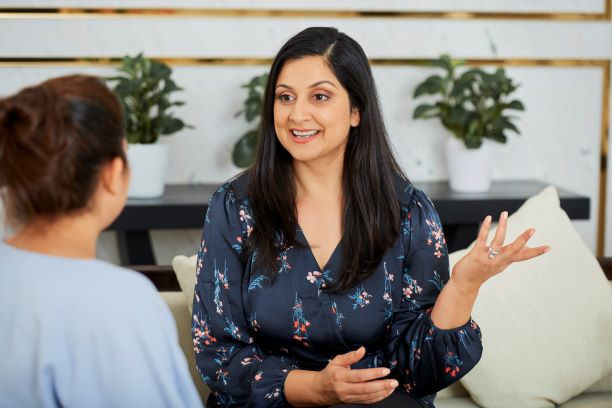

One on One Interviews
Most one on one meetings are for discovering and analyzing issues. Later, this will lead to problem solving meetings. These in turn will lead to decision making meetings. We cannot emphasize enough how important it is to learn as much as possible about the individuals you will meet. (Duration 7:14)

What Is Prospecting
Prospecting is the art and science of having inside salespeople in an organization make outbound calls, or use outbound contact channels, to generate sales leads. It is important to understand prospecting, as an essential part of business development. (Duration 3:51)

How To Prospect Successfully
There are four steps in prospecting which you must go through every time. Because without any exception, all potential clients have a need or business issues that can be solved with a professional solution. But they may or may not be aware of it, and if they are, may not be willing, or able, to pay for it. (Duration 16:00)

What Is A Sales Funnel
The sales process, called the funnel, moves in stages, from Suspects to Prospects, to Leads, and to Opportunities, which are either won or lost. The bottom of the sales funnel allows us to refresh our sales opportunities, with additional work at satisfied clients, and through referrals, and testimonials. (Duration 12:10)
How To Conduct Business Research
A wide variety of tools can be used to conduct business research. A treasure trove of data is available on the web, and in news and social media. In this module, we provide practical examples of how you can use widely available tools to conduct research on your clients and their industries. (Duration 15:25)

The 8 Types of Business Research
Research is fundamental to an understanding of clients and industries. There are eight different kinds of research and some can be, and often are, combined. To illustrate the differences between them, we will pair them up, and compare them, to help you get a better understanding of these methods and when to use them. (Duration 9:24)
Introduction to Robotics
A ‘Robot’ is defined as a reprogrammable. multifunctional manipulator, designed to move materials, parts, tools, or specialized devices, through various programmed motions, for the performance of a variety of tasks. We explore through examples what robots are, and the science of robotics. (Duration 5:25)

Major Fields of Applied Robotics
Robotics usage can be classified in 5 major areas: industrial; military; medical; space science; and domestic. We explain each of these, and why robots are suitable in these environments. We also explain some of the challenges. (Duration 3:42)

What Is Creative Problem Solving
Creative problem solving, (also known as CPS) enables you to get fresh perspectives. This helps you to develop innovative solutions to overcome obstacles in solving problems. It groups them into different areas and encourages more open exploration and thinking ‘outside the box’, before narrowing them down to potential solutions. (Duration 9:04)

Detailed Solutioning Approaches
Even though this is a word which is sometimes disputed as invalid by some English purists, it means the process of finding a solution to a problem. It is about innovation and creativity, on how to create new products and services. And finding faster and better ways to do things. (Duration 15:06)

High-level Solutioning Approaches
Innovation requires drive and discipline, to select and execute the best ideas and solutions. In this module, we walk you through the six steps you must follow to maintain that structure and discipline. (Duration 6:33)

Innovation and Creativity in Solutioning
Many companies want to be innovative, but few succeed. In most cases, this is a result of embracing the status quo, and to keep using the same approach for as long as it seems to be working. For many organizations, once the old approach no longer works, it is too late to start something new. Innovate or die. (Duration 9:18)

Elements of Successful Teams
To quote Michael Jordan: “Talent wins games but teamwork wins championships.” There are several key elements to make teamwork successful. Without these, several problems and issues are likely to surface during the lifecycle of any project. We explore and explain these key elements. (Duration 6:53)

Habits of Highly Effective Teams
Jason Rosenstein, co-founder of Asana, introduces the concept of the 3 C’s to explain the habits of highly effective teams. The 3 C’s are all to do with Clarity: Clarity of Purpose; Clarity of Plan; and Clarity of Responsibility. We explore these and elaborate on what it takes to make teams successful. (Duration 5:19)

Effective Team Communication
Communication is the cornerstone of all team efforts. Any deficiency in the communication process can have an incredibly significant impact on the success of a project, or on any other undertaking. Poor communication is the primary cause of project failure 33% of the time. Learn more about how to achieve clarity through communication. (Duration 10:17)

The 5 Stages of Developing Teams
The classic view on team development is: Forming; Storming; Norming and Performing, with Adjourning recently added as a fifth stage. We examine this and an alternative view of team development. This will give you an insight into what to expect when you bring teams together. (Duration 6:36)

The 9 Steps to a Customer Journey
A timeline view is one of the most popular formats for customer journey maps. This allows marketers to identify the key touchpoints, states of mind, actions, as well as the goals and motivations of a buyer, at specific points in time. We explain the nine essential steps in creating any customer journey map. (Duration 7:31)

How Does a Customer Journey Map Work
The customer journey mapping process involves gathering a vast amount of data about the buyer or prospect, from many sources. Many tools are available to do this. The main purpose is to identify the key interactions a customer has, from the first moment to the buying decision and beyond. (Duration 4:19)

How to Create a Customer Journey Map
The most popular approach to creating a customer journey map is using a timeline. This has 5 elements and 9 steps. We explain these here. (Duration 17:20)

Benefits of a Customer Journey Map
Customer journey mapping, allows us to streamline the gaps, and inconsistencies, between marketing communications, and product purchase, or service delivery, and it allows us to predict and manage customer behavior on a consistent basis, by tying a buyer’s pain points and actions to their specific needs. (Duration 1:49)

What is a Customer Journey Map
A Customer Journey Map is a highly detailed map, or flow, of the journey that a customer goes through before, during, and after deciding to acquire a product or a service. It is also called a user journey map, or customer experience map. It is a crucial step to understand how customers interact with you, and how to improve their experience. (Duration 4:42)

Elements of a Customer Journey Map
There are five essential elements that should be represented in any customer journey map. These are: Persona; Timeline, Emotion; Touchpoints; and Channels. Learn more about each here. (Duration 4:38)

Introduction to IoT
The Internet connects all people, so in a way we can call it the internet of people. Yet there are billions of devices that have readers, sensors, microchips, and cameras, that either already have or can have connectivity. So, we can also say that the internet is “the Internet of Things”. (Duration 5:19)

IoT Applied to Industry
After surpassing the number of people on the planet in 2008, IoT connected devices will reach 50 billion by 2020. That is 7 to 8 devices for every person. Many industries and sectors use IoT to innovate around existing and new products. We examine some key examples for a clear view of the current use and possibilities of IoT. (Duration 6:49)

IoT Compared and Contrasted to Cloud
Some confusion exists about IoT and Cloud. While these are complementary, they are not the same. For instance, IoT deals with real world devices, while Cloud deals with virtual concepts around real things. Both are enabling technologies for digital transformation. We compare them with examples. (Duration 1:39)

The Digital Transformation Blueprint
What are the nuts and bolts that help you make digital transformation work in your own organization? What are the interconnected parts, and what are their dependencies, and impact on each other? This module introduces you to the essential elements that should feature in your DX blueprint. (Duration 7:45)

Making DX Work in Your Organization
Digital transformation in any company is never easy. Much depends on the readiness of the people, the culture, and the maturity of the company’s DX readiness. Successful companies, in a mature transformation stage, follow eight essential steps. We explain them here. (Duration 15:46)

How to Start the DX Journey
So, what is necessary, to take on the transformation journey? Firstly, you need to identify the right digital initiatives, by designing a digital strategy. This has four phases or key elements to consider. Learn more about the four phases here. (Duration 6:12)

Transforming to The Digital Enterprise
Digital transformation sits at the top of the agenda for enterprises. It is not easy. Technology is at the core of every digital transformation, with the need to carry out digital transformation bringing with it unprecedented change. However digital transformation is not just about technology. Instead, it uses technology as a means to an end. Other factors are equally important. (Duration 8:23)

How Do Companies Use DX to Better Engage Customers
Ultimately, customers are the losers when the experience either becomes or remains disconnected. Their journey is rife with friction and inconsistent experiences. Digital transformation requires more than the intention to invest in the relevant digital channels that connected customers are using. It also requires more than the camaraderie or collaboration between distributed marketing teams. (Duration 1:38)

The Six Stages of DX and Their Six Support Pillars
There are six stages to digital transformation. In each of the stages, six support pillars enable the change. These support pillars (including Governance and Leadership, People and Operations, and Customer Experience) change their attributes as the organization matures in its DX efforts. This module offers a detailed look at the 6 stages, and the state of the support pillars during each. (Duration 17:37)

The Top Challenges of DX
Company culture is the basis of digital transformation, and people are at the heart of the change. But that it not the only challenge. Here, we elaborate on the other top challenges that can cause your DX efforts to stall or fail. (Duration 2:06)

Who Leads The DX Efforts?
Over the last few years, the CIO has slipped into third place, behind the CEO and the CMO. While technology remains important, it has shifted to being an enabler instead of a driver. It serves the multifunctional teams who bring all relevant skills, views, and experience to the table. We see the emergence of a new role, the Chief Digital Officer, leading DX efforts from the top. (Duration 2:02)

What Are the Success Factors of DX?
There are at least 7 critical success factors for digital transformation. These include Strategic Intent, Willingness to Invest, and the need to be Business Driven. This module offers a summary of the success factors and why they are important. (Duration 2:07)

Why Embark on the DX Journey
From the early adopters of DX, we see that even though new business models and increased efficiency or productivity are important, the primary driver and motivator is that it is all about the customer. It is about offering new and different ways to market, sell, upsell, cross-sell, anticipate needs, and serve them better. (Duration 5:13)

Advantages and Disadvantages of Matrix Organizations
Matrixed organizations have been around for some time now and are well-practiced in several forms. Yet each has its advantages (for instance, breaking silo thinking, leveraging expert and local knowledge). And each has its disadvantages (Notably ambiguity and the inevitable conflicts that arise). We explore and explain these in this module. (Duration 9:37)

Leadership Skill Success Factors in a Matrix
Managing in a matrix is more of an art than a science. Engagement and empowerment are far more important than centralized oversight. The art comes from empowering and coaching individual participants over which no one has sole control. (Duration 11:52)

Required Skills in a Matrix
To work effectively as a functional resource manager or as a project manager in a matrix structure requires many skills. Among these are: influence; self-management; collaboration; and empathy. We explore these and other key skills required. (Duration 2:32)

Types of Project Matrix Organization
There are three different types of structures, depending on the level of authority assigned to functional and project managers. These are the weak, balanced, and strong matrix organization structures. We explain each and provide examples. (Duration 4:46)

The 9 Sections of The Business Model Canvas
The Business Model Canvas (BMC) is an extremely hands-on tool that helps overall understanding of the business. It spurs healthy discussion, fosters creativity, and requires careful analysis. The tool has 9 sections, which form the building blocks of a business model. We explain these in detail here. (Duration 17:33)

The Business Model Canvas for Startups and Entrepreneurs
Using the BMC for startups and entrepreneurs is as relevant as using it for established companies. The keys to success in this case are:
- Visualize the business model
- Keep the model up to date, agile, and responsive
- Take the guesswork out and replace with a dose of reality
Learn more about these here (Duration 4:29)

Elements of The Business Model Canvas
The elements of the BMC describe a firm or product’s value proposition, infrastructure, customer base, and financial structure. They support a clean “strategy on a page” view of the business, proposition, opportunity, or product. (Duration 6:08)

What Is The Business Model Canvas
The Business Model Canvas introduces a systematic approach to focus on a business model segment by segment. It allows for a clean review and discussion by brainstorming the segments, one by one, to compare severaloptions or paths required to innovatively impact the business model. (Duration 7:41)

A Brief Introduction to Waterfall
Waterfall is ideal for projects where documentation is important or even crucial. If someone leaves during the project, the next person can pick up where they left off by familiarizing themselves with the documentation. Prior to Agile, Waterfall was often used for software development, but has now fallen out of favor. Learn why here. (Duration 1:32)

Introduction to Agile
Let us introduce you to the essence of Agile. In an agile project:
- The focus is on getting the most business value
- Decisions are value driven
- The product or process owner is responsible for the success of the project
(Duration 10:01)

Plan-driven versus Adaptive Project Management
The differences can most easily be summarized as follows. In a traditional project, the project manager directs the team and plays a very active role in leading the team. In an agile project, the team is empowered and self-organizes, and the scrum master is a facilitator. (Duration 14:44)

The Hybrid Agile Approach
In hybrid project management, the agile project manager needs to apply a mix of agile and project management principles and practices, in the right proportions and with the right balance. This includes an iterative and adaptive approach in situations where this is required. (Duration 2:13)

Aside From Systems Thinking, What Are The Other Types
There are other types of thinking besides Systems Thinking. Some key examples we explore here are:
- Linear Thinking
- Event-oriented Thinking
- Lateral Thinking
- Critical Thinking
(Duration 2:08)

How To Use Systems Thinking
Systems Thinking provides us with alternatives to solve problems by expanding the thinking process and to define and articulate problems in different ways. It makes is also realize that there are no perfect answers. Learn how to apply Systems Thinking here. (Duration 22:44)

What Is Systems Thinking
Systems Thinking is an innovative way to look at what we see and to construct a mental framework of it. The entity or construct is looked at as a whole, keeping in mind its functioning in relationship to a larger context or to the environment. (Duration 13:05)

Why and When to Use Systems Thinking
Typical problems which are considered ideal for Systems Thinking exploration have the following characteristics. They are:
- Very important to the organization
- Of a chronic and recurring nature
- Familiar and well-known to key stakeholders
- Unresolved
(Duration 3:09)

How to Use a Balanced Scorecard
We explore in some detail the 5 stages of using the Balanced Scorecard:
- Prepare, define, and communicate the strategy
- Decide what to measure
- Finalize and implement the plan
- Widely communicate and use the results
- Review, amend, and enhance the BSC system
(Duration 5:02)

What is a Balanced Scorecard
The Balanced scorecard is a strategy performance management tool, in a semi-standard structured form. It is used by managers to keep track of the execution of activities by employees within their span of control, and to monitor the consequences and results arising from their work.
(Duration 9:30)

What is The Blue Ocean Strategy and How Does it Work
The Blue Ocean Strategy challenges companies to stay out of the red ocean of bloody competition by creating an uncontested market space. This renders the competition irrelevant or at least defers their market entry. Companies can get out of the red ocean and stand out by focusing on innovation that creates a whole new market for them. (Duration 8:33)

The 5 Steps of The Blue Ocean Strategy Shift
We describe the five steps, and their associated tools, for making the shift:
- Getting started
- The state of play
- What could be
- A structure for blue ocean creation
- Making the move
(Duration 18:27)

What Is The Blue Ocean Strategy Shift
A successful blue ocean shift has the following three characteristics:
- Adopt blue ocean perspectives
- Practical tools to guide the process
- Embrace the concept of humanness
(Duration 6:52)

10 Important Things to Look For When Using Consultants
Often, the world of consulting is looked upon as if it is shrouded with a veil of mystery and secrecy. We reveal ten points about consulting that shed some light on things you perhaps never knew or were not sure about. (Duration 6:44)

The Reluctance to Use Consultants
The reluctance of companies to use consultants covers a predictable spectrum of beliefs:
- Many businesses are highly specialized
- They believe consultants have their own agendas
- They’re too expensive, and the benefits are not clear
- Their business model conflicts with the company’s
(Duration 5:28)

What Is Consulting and Who Are The Top Firms
Consulting is giving expert advice or guidance in different fields such as business, technology, education, law, regulatory compliance, human resources, marketing, finance, health care, engineering, science, security, or any of many other specialized areas. Consultants use their niche or broad experience, their industry understanding, and their problem-solving abilities to offer valuable advice and solutions to problems and issues. (Duration 9:21)

Why Do We Use Consultants
They are experienced, and in some cases even renowned experts in their field. Because of their length of experience, they have seen the problem you face for the first time, multiple times over. We explore seven reasons why companies use consultants in this module. (Duration 6:40)

How Do We Manage Project Risk
Our planned risk response should be in balance with how significant the risk is. Typically, there are four response categories we should focus on:
- Avoid the risk by reducing its likelihood to zero
- Transfer the risk to a third party
- Mitigate the risk by reducing its likelihood as much as possible
- Accept the risk and assign contingency resources
(Duration 11:13)

Identifying and Evaluating Project Risk
Even before we formally start any project, we should identify any potential risk, and develop a strategy for managing the project risk. We explore three things to do here:
- Learn from the past
- Poll your team members and stakeholders
- Record and manage all risks in a risk register
(Duration 13:01)

What Is Project Risk Management
Whatever we do in business involves some level of risk, regardless of the activity. Risk should be analyzed, assessed and contemplated against whatever the potential benefits, rewards, or other positive outcomes. Companies need to be equipped to decide which risk is acceptable, and which risks to avoid. We explore project risk management in detail. (Duration 12:08)